Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Introduction
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the downloadable TODO ADD FILE REFERENCE ExcelWriter_Basic_Tutorials.zip, there is a completed template file located in ComleteFinancialReportCompleteFinancialReport/templates/Part1_Financial_Template.xlsx. A copy of the completed template file is also available TODO ADD FILE REFERENCE. |
Getting Started
In this tutorial ExcelTemplate is being used to populate data and ExcelApplication is being used to format the dataapply some formatting and merge workbooks together. This part of the tutorial will make demonstrate how to use of data marker modifiers and ordinal syntax in ExcelWriter templates.
| Note |
|---|
This example assumes an understanding of ExcelTemplate. If you are not familiar with how to set up an Excel template with data markers, please go through the Simple Expense Summary first. |
...
Setting Up the Template
Using Ordinal Syntax
Here is the starting template: 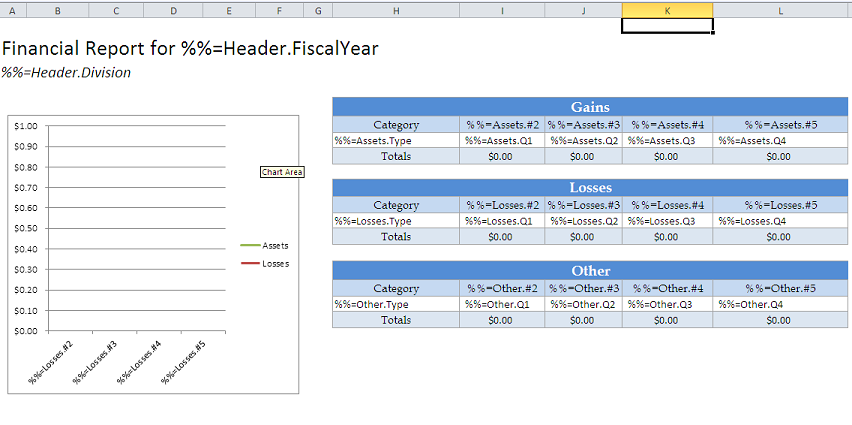
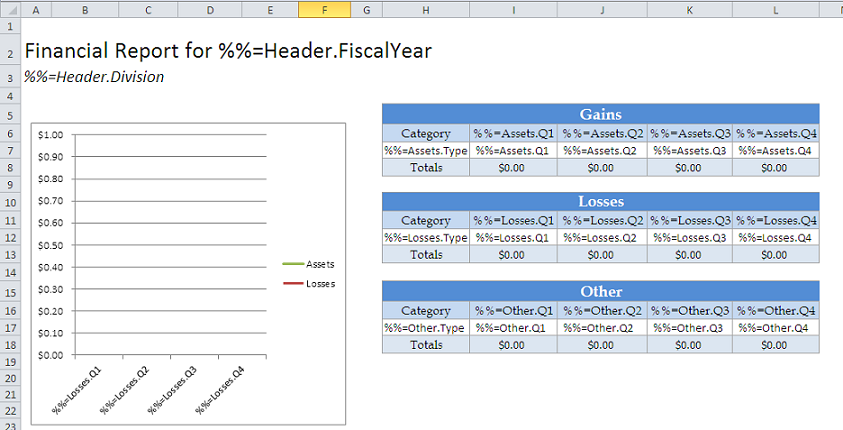
The next few steps will demonstrate adding modifiers. This template show the process of using ordinal syntax.
ExcelTemplate normally requires the data marker for a column of data to specify the data set and the column name (e.g. %%=DataSource.ColumnName). In the event that the column name or data source name is unknown, ExcelWriter supports the use of ordinal numbering based on the data source column.
Instead of binding to to a specific column name, "%%=Assets.Q1", the column name can be replaced with ordinal syntax, "%%=Assets.#2". This denotes the second column in the 'Assets' data set. The data set name can also be replaced, "%%=#3.#2", which denotes the second column from the third data source bound to the template.
However, in this example, we will only change the column name, as shown below:

Using Data Marker Modifiers
In addition to ordinal syntax, ExcelWriter supports data marker modifiers, which are tags that change how and what data is imported into the file. This template uses two different data marker modifiers - fieldname and optional. Modifiers are added in parentheses at the end of a data marker. They alter the binding behavior of the data marker.
The fieldname modifier shows the fieldname field name of the column being bound. It will not bind any additional data. It is used like thisThe syntax is as follows:
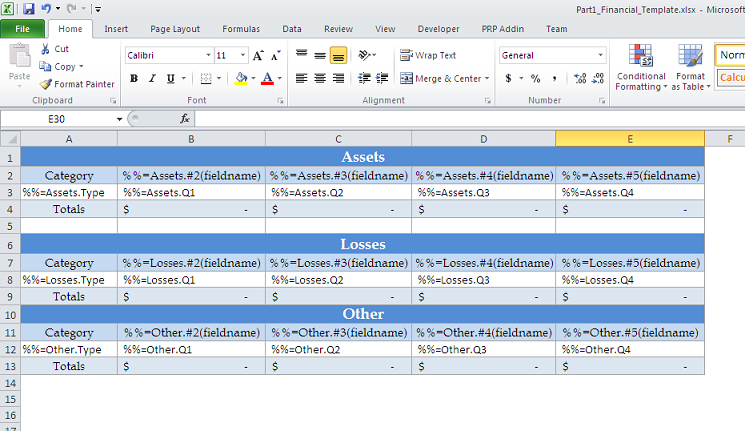
The optional modifier allows that The optional modifier allows the data marker to be ignored on data binding. The optional modifier allows you to bind data if the column might be empty. It is used like this:
if there is no data corresponding with that column. This is just an ignore - the column itself will still exist, but the data marker will be skipped. Here is a usage example:

In the above, the "Division" column will be ignored if no division data is available.
After the modifiers are added, the template should resemble this: 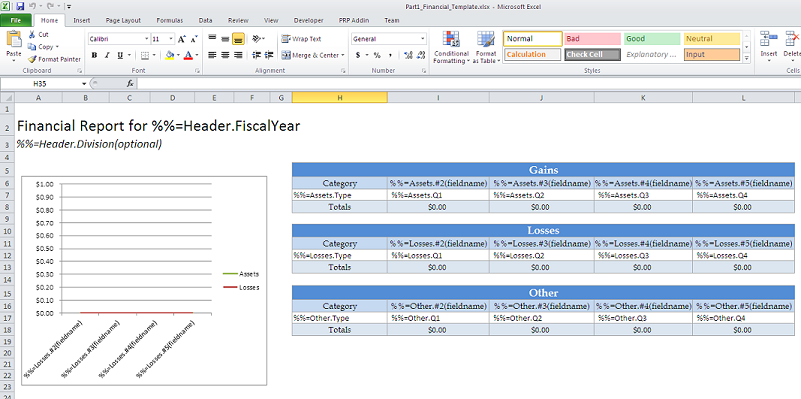
Conditional Formatting
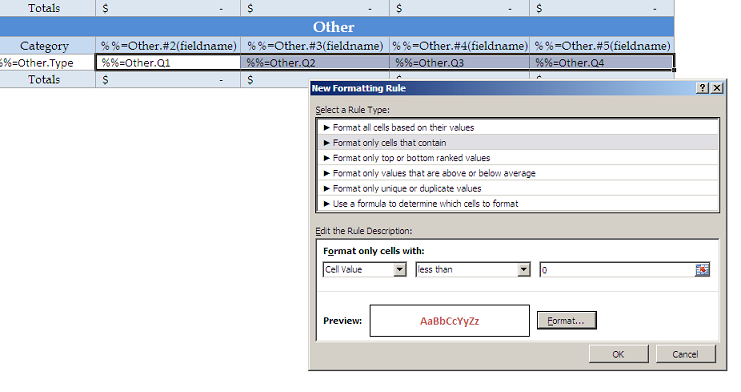
ExcelTemplate will persist conditional formatting in a template. In this tutorial, conditional formatting is applied to the "Other" table. It sets negative numbers to be red and bold.
1. On the "Home" tab in Excel, click on "Conditional Formatting"
2. Select "New Rule..."
3. In this tutorial the condition type is "Format only cells that contain..." The rule is "Cell value less than 0"
4. Click on "Format..." Set the text to be dark red. Set the typeface to be bold.
5. Click OK to save the rule.
Adding an ExcelWriter Reference in Visual Studio
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the sample code, the reference to SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter.dll has already been added to the CompleteFinancialReport project. |
...
- Open Visual Studio and create a .NET project.
- The sample code uses a web application.
- Add a reference to SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter.dll
- SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter.dll is located under Program Files > SoftArtisans > OfficeWriter > dotnet > bin
Writing the Code
1. Include the SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter namespace in the code behind
| Code Block |
|---|
using SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter;
|
...
3. Open the template file with the ExcelTemplate.Open method.
| Code Block |
|---|
XLT.Open(Page.MapPath("//templates//Part1_Financial_Template.xlsx"));
|
4. Create a DataBindingProperties object. None of the binding properties will be changed for this tutorial, but DataBindingProperties is a required parameter in ExcelTemplate data binding methods.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataBindingProperties dataProps = XLT.CreateDataBindingProperties();
|
Data Binding
1.Get the data for the Assets, Losses, and Other datasets
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the sample project, we are parsing CSV files with query results, rather than querying a live database. The CSV files are available under the data directory. There is a copy of the CSV parser, |
These calls are to a helper method GetCSVData that parses the CSV files and returns a DataTable with the values.
If you are following in your own project and would like to parse the CSV files as well, you will need to:
- Add a reference to
GenericParsing.dll - Include
GeneringParsingat the top of your code. - Add the
GetCSVDatamethod that can be found in the sample code.
1.Get the data for the Assets, Losses, and Other datasets
These calls are to a helper method GetCSVData that parses the CSV files and returns a DataTable with the values.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataTable dtAssets = GetCSVData("//data//Assets.csv"); DataTable dtLosses = GetCSVData("//data//Losses.csv"); DataTable dtOther = GetCSVData("//data//Other.csv"); |
2. Create the datasets for the header row. Recall the optional modifier for the "Division" tag. This tutorial will not bind any data for that tag to demonstrate the function.
| Code Block |
|---|
//Create the array of header values. This example only binds a single item string[] headerValues = { "2011" }; //Create the array of header names. string[] headerNames = { "FiscalYear" }; |
3. Use ExcelTemplate.BindData to bind the data for the Top and Details Sales Assets, Losses, and Other data sets.
| Code Block |
|---|
XLT.BindData(dtAssets, "Assets", bindingProps); XLT.BindData(dtLosses, "Losses", bindingProps); XLT.BindData(dtOther, "Other", bindingProps); |
4. Use the ExcelTemplate.BindRowData method to bind the header data to the data markers in the template file (i.e. %%=Header.FiscalYear).
| Code Block |
|---|
XLT.BindRowData(headerValues, headerNames, "Header", bindingProps);
|
5. Call ExcelTemplate.Process() to import all data into the file.
| Code Block |
|---|
XLT.Process();
|
Do not save the file. In the next step the XLT object will be processed by ExcelApplication.
Without the post processing, the populated file will persist the column width and heights. It should look something like this: 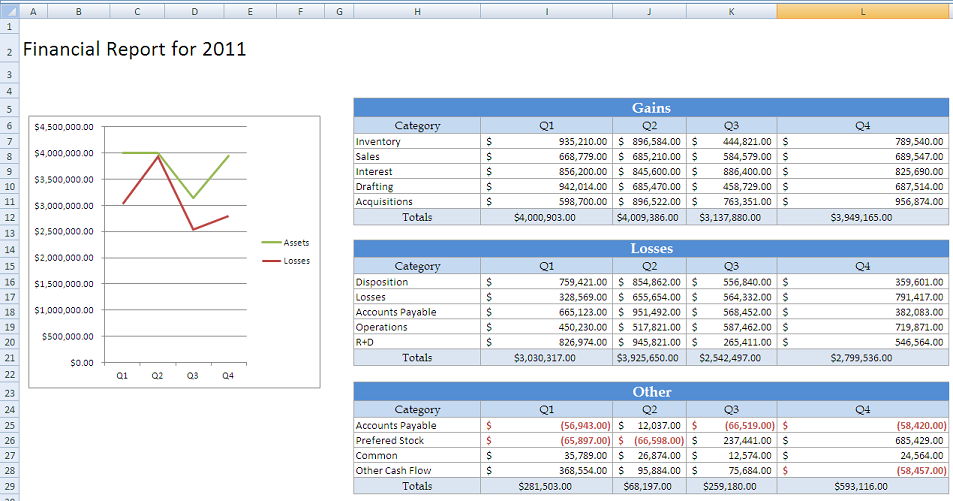
Post-Processing
1. In the post-processing method, instantiate the ExcelApplication object:
| Code Block |
|---|
ExcelApplication XLA = new ExcelApplication();
|
2. Open the populated file with ExcelApplication. The file will open as a Workbook object
| Code Block |
|---|
Workbook wb = XLA.Open(XLT);
|
3. Access the first Worksheet.
| Code Block |
|---|
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0];
|
4. Call Area.AutoFitHeight() and Area.AutoFitWidth() to set the column and row height. AutoFitWidth sets the column width to fit the widest populated cell in the column. AutoFitHeight sets the row height to highest populated cell in the row. In this snippet, the area is Worksheet.PopulatedCells, which returns an area containing all populated cells.
| Code Block |
|---|
ws.PopulatedCells.AutoFitWidth();
ws.PopulatedCells.AutoFitWidth();
|
5. Finally, call ExcelApplication.Save to save the final file. This example streams the file using the page response.
...
6. Call ExcelTemplate.Save() to save the final output
| Code Block |
|---|
XLT.Save(Page.Response, "temp.xlsx", false); |
The final output should look something like this: 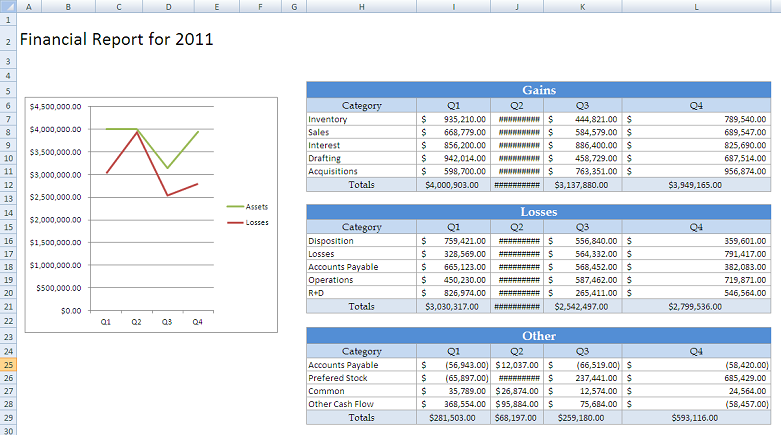
Final Code
| Code Block |
|---|
using SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter; using GenericParsing; ... //Instantiate the template object ExcelTemplate XLT = new ExcelTemplate(); //Open the file XLT.Open(Page.MapPath("//templates//Part1_Financial_Template.xlsx")); //Create data binding properties DataBindingProperties bindingProps = XLT.CreateDataBindingProperties(); //Get the data from the CSVs. More info about the generic parser is available //in the project and in the tutorial above. DataTable dtAssets = GetCSVData("//data//Assets.csv"); DataTable dtLosses = GetCSVData("//data//Losses.csv"); DataTable dtOther = GetCSVData("//data//Other.csv"); //Declare the row data. This tutorial uses a single item array to demonstrate the //optional modifier string\[\] headerValues = { "2011" }; string\[\] headerNames = { "FiscalYear" }; //Bind each datatable XLT.BindData(dtAssets, "Assets", bindingProps); XLT.BindData(dtLosses, "Losses", bindingProps); XLT.BindData(dtOther, "Other", bindingProps); //Bind the single row data XLT.BindRowData(headerValues, headerNames, "Header", bindingProps); //Call process to import data to file XLT.Process(); /*This next section handles the post-processing*/ //Instantiate ExcelApplication ExcelApplication XLA = new ExcelApplication(); //Open the XLT object as a new workbook Workbook wb = XLA.Open(XLT); //Get the first worksheet Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[0]; //Set the autofit width and height ws.PopulatedCells.AutoFitWidth(); ws.PopulatedCells.AutoFitHeight(); //Save the file XLAXLT.Save(wb, Page.Response, "temp.xlsx", false); |
Downloads
TBA
You can download the code for the Financial Report here.
Next Steps
Continue to Part 2: Sub-Report with Number FormatsUsing Styles and Formatting