This is Part 2 of the two-part tutorial series <i>Extended Sales Summary<i> scenario. It is recommended that you complete Part 1 - Copying Sheets before starting this section. |
The sample code template (template.xlsx), page (Part2_CSV.aspx), and code behind (Part2_CSV.aspx.cs) are included in the ExtendedSalesSummary project available for download as part of the ExcelWriter Basics Tutorials. |
This part focuses on using ExcelApplication to create and populate a coversheet that includes user-supplied name, the current date, and a selected picture. It also includes data binding with ExcelTemplate.
Because this part of the tutorial demonstrates further capabilities of ExcelApplication, the code behind will be modified.
Writing the code for the cover sheet comes in two parts. the first part uses ExcelApplication to create a coversheet; and the second part uses ExcelTemplate to bind the appropriate data to the data markers on the cover sheet.
We want to create a cover sheet that looks like the following Excel worksheet:
Ultimately, the cells below the Table of Contents will be populated with hyperlinks to country sheets in the workbook. The logo will be selected from the front end. The "Report For :" field will correspond with the supplied name, and finally, the "Date Executed :" will correspond with today's date.
1. Following the line {{wb.Worksheets0.Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden; }}, use the Worksheets.CreateWorksheet method to create a new worksheet called "Summary" at the beginning of the workbook:
wb.Worksheets.CreateWorksheet("Summary", 0); |
2. Create a Worksheet object of the worksheet that was just created.
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets["Summary"]; |
3. Hide the gridlines in the summary worksheet using Worksheet.ShowGridlines. By default, this property is set to true.
ws.ShowGridlines = false; |
4. Create a GlobalStyle using the Workbook.CreateStyle() method. ExcelWriter uses three Styles: CellStyle. GlobalStyle, and NamedStyle. The GlobalStyles type is a Style that can be applied to cells and areas throughout the workbook.
newcode}}GlobalStyle underlined = wb.CreateStyle();{{newcode
5. Set the underlined GlobalStyle to Font.UnderlineStyle to Single. ExcelApplication allows for various underline types.
underlined.Font.Underline = Font.UnderlineStyle.Single; |
6. Create another GlobalStyle using the Workbook.CreateStyle() method called 'boldAndFont12'.
GlobalStyle boldAndFont12 = wb.CreateStyle(); |
7. Use the Style.Font to set the style font to 'Bold' and 'Size to 12.
boldAndFont12.Font.Bold = true; boldAndFont12.Font.Size = 12; |
8. Use the Cell.Value method to set the value of cell A15 to the string "Date Executed :". Cell.Value must be a string.
Use the Cell.Value method again to set the value of cell A16 to the string "Report For :" and value of cell A18 to "Table of Contents".
ws.Cells["A15"].Value = "Date Executed :"; ws.Cells["A16"].Value = "Report For :"; ws.Cells["A18"].Value = "Table of Contents"; |
9. Create another GlobalStyle called "dateForm" and use the NumberFormat.DateFormat method to create the desired date format.
GlobalStyle dateForm = wb.CreateStyle(); dateForm.NumberFormat = wb.NumberFormat.DateFormat.MonthDayYear; |
10. Apply the styles to the various cells.
ws.Cells["A15"].Style = underlined; ws.Cells["A16"].Style = underlined; ws.Cells["A18"].Style = boldAndFont12; ws.Cells["B15"].Style = dateForm; |
11. Insert the data markers for the WebFormData (Textbox inputted name, and today's date) as strings. Data markers must have the format %%=DataSource.ColumnName
ws.Cells["C16"].Value = "%%=WebFormData.Name"; ws.Cells["C15"].Value = "%%=WebFormData.Date"; |
12. Iterate through the country sheet names using a for loop, excluding the "Summary" and hidden "SimpleTemplate" sheets.
Cells below the "Table of Contents" cell are given a Hyperlink formula to another sheet in the workbook. When hyperlinking to another page in a workbook, the formula must follow "=HYPERLINK(\"#DestinationSheet!DesitinationCell\", \"Text\")" and use the Cell.Formula method.
for (int i = 2; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
string sheetName = wb.Worksheets[i].Name.ToString();
ws.Cells[16 + i, 1].Formula = "=HYPERLINK(\"#"+sheetName+"!A1\", \""+sheetName+"\")";
}
|
13. Finally, we want to insert a picture into the cover sheet. This requires creating an Anchor object using the Worksheet.CreateAnchor() method.
Anchor anc = wb.Worksheets[0].CreateAnchor(0, 0, 0, 0); |
14. We then want to create a Picture object using Pictures.CreatePicture method where the string describing the name of the image is pulled from the utility method RBImage.SelectedItem.Value.
string image = RBImage.SelectedItem.Value; Picture logo = ws.Pictures.CreatePicture(Page.MapPath(@image), anc); |
15. We want to set the dimensions of the Picture object using Picture.Height and Picture.Width.
logo.Height = 195; logo.Width = 290; |
16. Finally, we want select the first sheet in the workbook (the "Summary" sheet) to be first viewed when the document is opened.
wb.Worksheets[0].Select(); |
1. Following the lines in the code of Part 1,
for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
BindCountryData(wb.Worksheets[i].Name);
}
|
string name = TextBox1.Text;
This is another utility method. |
2. Create an string array for the header values and a string array for the column names.
ExcelTemplate can be bound to numerous types of .NET data structures: single variables, arrays (1-D, jagged, multi-dimensional), DataSet, DataTable, IDataReader etc. The source of the data can come from anywhere.
Some of the aforementioned structures have built in column names, such as the DataTable. When working with arrays, which don't have built in column names, you have to define the column names in a separate string array.
string[] coverData = {name, DateTime.Now.Date.ToString("M/dd/yyyy")};
string[] coverMarkers = { "Name", "Date" };
|
3. Use the ExcelTemplate.BindRowData method to bind the web form data to the data markers in the template file (%%=WebFormData.Name, %%=WebFormData.Date) with blank DataBindingProperties.
BindRowData() binds a single row of data to the template, but the data markers in the template do not need to be in a single row.
xlt.BindRowData(coverData, coverMarkers, "WebFormData", xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties()); |
4. Now run your code.
Here is an example of what the form will look like.
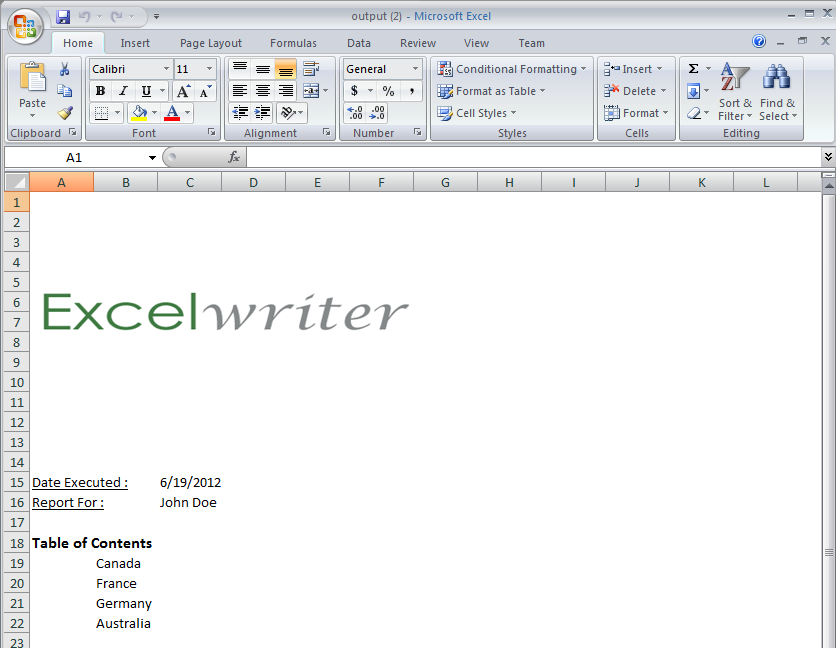
Notice that the countries in the Table of Contents are hyperlinked to the corresponding sheets in the workbook.
using SoftArtisans.Office.ExcelWriter;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Collections.Generic;
...
protected void Main(object sender, EventArgs e){
ExcelApplication xla = new ExcelApplication();
Workbook wb = xla.Open(Page.MapPath(@"templates\template.xlsx"));
for (int i = 0; i < selectedCountries.Count; i++)
{
wb.Worksheets.CopySheet(wb.Worksheets[0], wb.Worksheets.Count, selectedCountries[i]);
}
wb.Worksheets[0].Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden;
wb.Worksheets[1].Select();
wb.Worksheets.CreateWorksheet("Summary", 0);
Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets["Summary"];
ws.ShowGridlines = false;
GlobalStyle underlined = wb.CreateStyle();
underlined.Font.Underline = Font.UnderlineStyle.Single;
GlobalStyle boldAndFont12 = wb.CreateStyle();
boldAndFont12.Font.Bold = true;
boldAndFont12.Font.Size = 12;
ws.Cells["A15"].Value = "Date Executed :";
ws.Cells["A16"].Value = "Report For :";
ws.Cells["A18"].Value = "Table of Contents";
GlobalStyle dateForm = wb.CreateStyle();
dateForm.NumberFormat = wb.NumberFormat.DateFormat.MonthDayYear;
ws.Cells["A15"].Style = underlined;
ws.Cells["A16"].Style = underlined;
ws.Cells["A18"].Style = boldAndFont12;
ws.Cells["B15"].Style = dateForm;
ws.Cells["C16"].Value = "%%=WebFormData.Name";
ws.Cells["C15"].Value = "%%=WebFormData.Date";
for (int i = 2; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
string sheetName = wb.Worksheets[i].Name.ToString();
ws.Cells[16 + i, 1].Formula = "=HYPERLINK(\"#"+sheetName+"!A1\", \""+sheetName+"\")";
}
Anchor anc = wb.Worksheets[0].CreateAnchor(0, 0, 0, 0);
string image = RBImage.SelectedItem.Value;
Picture logo = ws.Pictures.CreatePicture(Page.MapPath(@image), anc);
logo.Height = 195;
logo.Width = 290;
wb.Worksheets[0].Select();
xlt = new ExcelTemplate();
xlt.Open(xla, wb);
for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
BindCountryData(wb.Worksheets[i].Name);
}
string name = TextBox1.Text;
string[] coverData = {name, DateTime.Now.Date.ToString("M/dd/yyyy")};
string[] coverMarkers = { "Name", "Date" };
xlt.BindRowData(coverData, coverMarkers, "WebFormData", xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties());
xlt.Process();
xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false);
}
protected void BindCountryData(string selection)
{
DataBindingProperties dbp = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties();
dbp.WorksheetName = selection;
string[] specificInfo = { "FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", selection };
string[] headerTitles = { "FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" };
xlt.BindRowData(specificInfo, headerTitles, "Header", dbp);
DataTable dts = Sales(selection, "TOP 5");
DataTable dts2 = Sales(selection, "");
xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dbp);
xlt.BindData(dts2, "Details", dbp);
}
public static DataTable Sales(string selection, string topORall)
{
//Create the query
string queryString = "USE AdventureWorks2008R2; " +
"DECLARE @find nvarchar(100); " +
"SET @find ='" + selection + "'; " +
"SELECT " + topORall + " Sales.Store.Name AS Description, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TotalDue AS Sales FROM Sales.Store " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.Customer ON Sales.Store.BusinessEntityID = Sales.Customer.StoreID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.Customer.CustomerID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.CustomerID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID = Sales.Customer.TerritoryID " +
"WHERE DATEPART(yyyy, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate) = 2008 " +
"AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OnlineOrderFlag = 0 " +
"AND Sales.SalesTerritory.Name = @find " +
"ORDER BY Sales DESC;";
//Get connection
SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(@"Data Source=TS-IH03\SQL2008R2;Initial Catalog=ExcelApp2;Integrated Security=True");
//Assign command and associated connection
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(queryString, connection);
//Select data adapter
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
//Make a new table, fill it and return it
DataTable dtGet = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(dtGet);
return dtGet;
}
protected List<string> GetListBoxSelections(){
//Get the ListBox selections and make the appropriate number of copies
List<string> countryNames = new List<string>();
foreach (int i in ListBox1.GetSelectedIndices())
{
countryNames.Add(ListBox1.Items[i].Text);
}
return countryNames;
}
|
You can download the code for the Extended Sales Summary here.
*ExtendedSalesSummary_CSharp.zip