An Area object represents a rectangular set of cells. To create an Area object, call one of the following methods:
- Worksheet.CreateArea(Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32) - This method takes the 0-based indexes of the area's first row and column, and the number of rows and columns to include in the area.
- Worksheet.CreateArea(String) - This method takes a formula representing the area, for example, "=A1:G10". The formula is relative to the current worksheet.
- Worksheet.GetColumnProperties(Int32) - Get and edit column properties.
- Worksheet.GetRowProperties(Int32) - Get and edit row properties.
A Range is a collection of areas. The areas in a range may be non-adjacent, and a range can include areas in different worksheets. To create a Range (without a name), call one of the following methods:
- Workbook.CreateRange(String) - This method takes a formula representing the range, for example "=Sheet1\!A1:G10" defines a range containing one area and "=Sheet1\!B$12:$H$21 Sheet1\!$F$18:$K$29 Sheet1\!D$16:$M$21" defines a range containing three areas. The formula must be three-dimensional (i.e., it must specify the sheet or sheets).
- Workbook.CreateRange(Area()) - This method takes an array of Area objects representing the range.
- Worksheet.CreateRange(String) - This method takes a formula representing the range, for example "=Sheet1\!A1:G10" defines a range containing one area and "=Sheet1\!B$12:$H$21 Sheet1\!$F$18:$K$29 Sheet1\!D$16:$M$21" defines a range containing three areas. The formula must be three-dimensional (i.e., it must specify the sheet or sheets).
A NamedRange is stored in ExcelWriter's NamedRanges collections (Workbook.NamedRanges and Worksheet.NamedRanges) and is accessible after the workbook is saved. In Excel, named ranges are listed in the name box above the top-left corner of the worksheet.
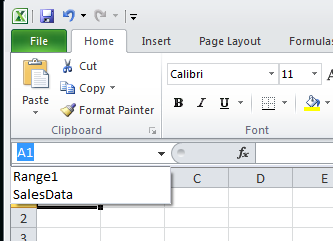
To create a named range, call one of the following methods:
Workbook.CreateNamedRange(String, String) - This method takes a formula representing the range, for example "=Sheet1\!A1:G10", and a name for the range. The formula must be three-dimensional (i.e., it must specify the sheet or sheets).
Workbook.CreateNamedRange(Area(), String) - This method takes an array of [Area] objects representing the range and a name for the range.
Worksheet.CreateNamedRange(Int32, Int32, Int32, Int32, String) - This method returns a named range that contains one rectangular area.
Worksheet.CreateNamedRange(String, String) - This method takes a formula representing the range, for example "=Sheet1\!A1:G10", and a name for the range. The formula must be three-dimensional (i.e., it must specify the sheet or sheets).
Importing Data to an Area
You can use an area as a set of target cells for imported data. The Area object's ImportData method allows you to import a block of data from a rectangular array or from an ADO.NET DataTable, DataView, or DataReader. To import data to an area:
Create an area in a worksheet.
Get a rectangular array, DataView, DataReader, or - as in the following example - DataTable to use as the data source.
Call ImportData to import the data. The method returns a new area containing the imported values.
For more information, see Importing Data.
Applying Formatting to Areas and Ranges
Defined styles can be assigned to cells, rows, columns, areas, and ranges. To assign a style to a range or area:
Create a style.
# Define an area or range, for example:
Set or apply the style.
For more information on setting and applying styles, see Styles.