Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
...
This tutorial assumes that the coder knows how to set up an Excel Template using data markers and Excel cell formatting. The .XLSX template file is available here.
ExcelTemplate vs. ExcelApplication
...
ExcelTemplate object is used for template-driven document generation. This object opens an ExcelWriter template file, populates it with data from a specified data source, and generates a new Excel workbook. An Excel file uploaded as an ExcelTemplate object is not directly modifiable at runtime.
...
The ExcelApplication
...
object is an Excel file engine that can be used to create, open, modify, and save workbooks. A single instance of ExcelApplication can generate multiple Excel workbooks.
This tutorial opens an Excel template file formatted as an for ExcelTemplate origin file (i.e. it contains formatted data markers) and makes customizations using ExcelApplication object. This means that the file can be copied based upon the , based on a user's specification using the ExcelApplication CopySheet method. This method copies a worksheet (including its formatted data markers) to another location in the workbook. The method has three parameters:
...
selections. In particular, it highlights the functionality of the CopySheet method. Then data is bound to the template using ExcelTemplate, again, based on a user's selections.
| Note |
|---|
This tutorial assumes a basic understanding of the |
Setting up the template
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the downloadable ExcelWriter_Basic_Tutorials.zip, there is a completed template file located in ExtendedSalesSummary/templates/template.xlsx. |
The template file should look something like this:
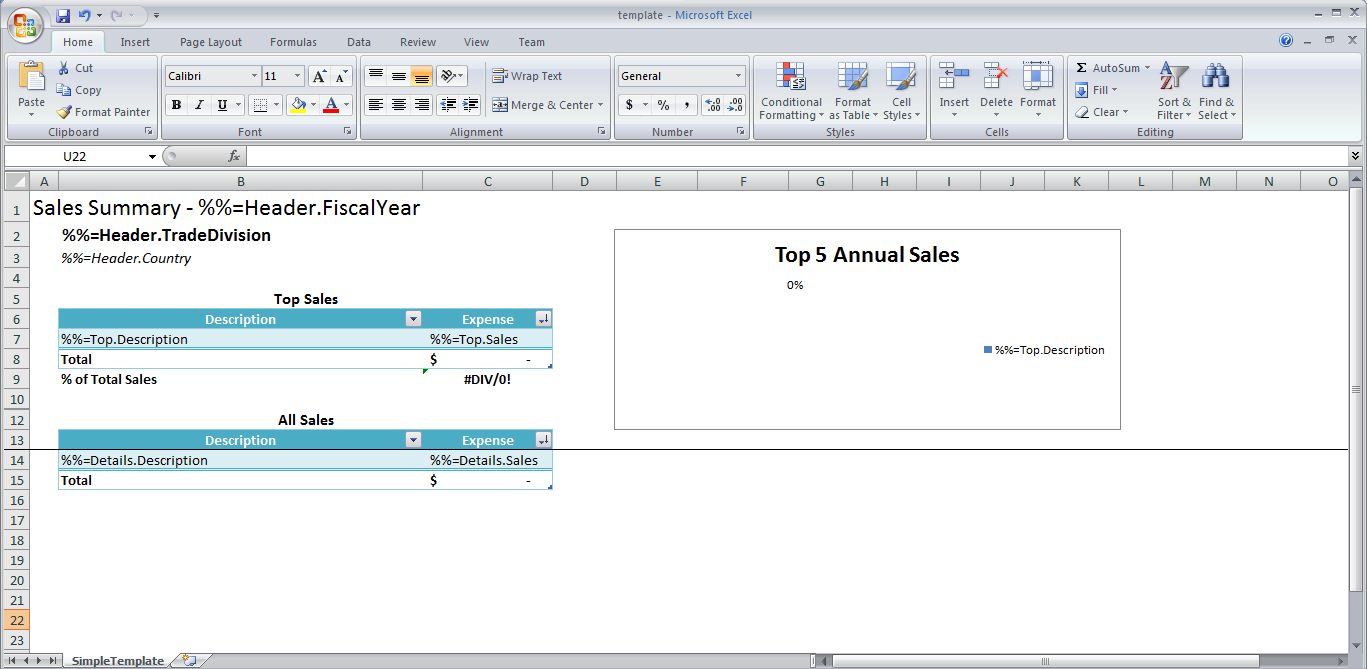
One advanced data marker format has been used in the above template. The data marker entitled Sales Summary - %%=Header.FiscalYear references another cell for the content. The below image is the data marker that was input and is how ExcelWriter will identify the appropriate fields to bind data.
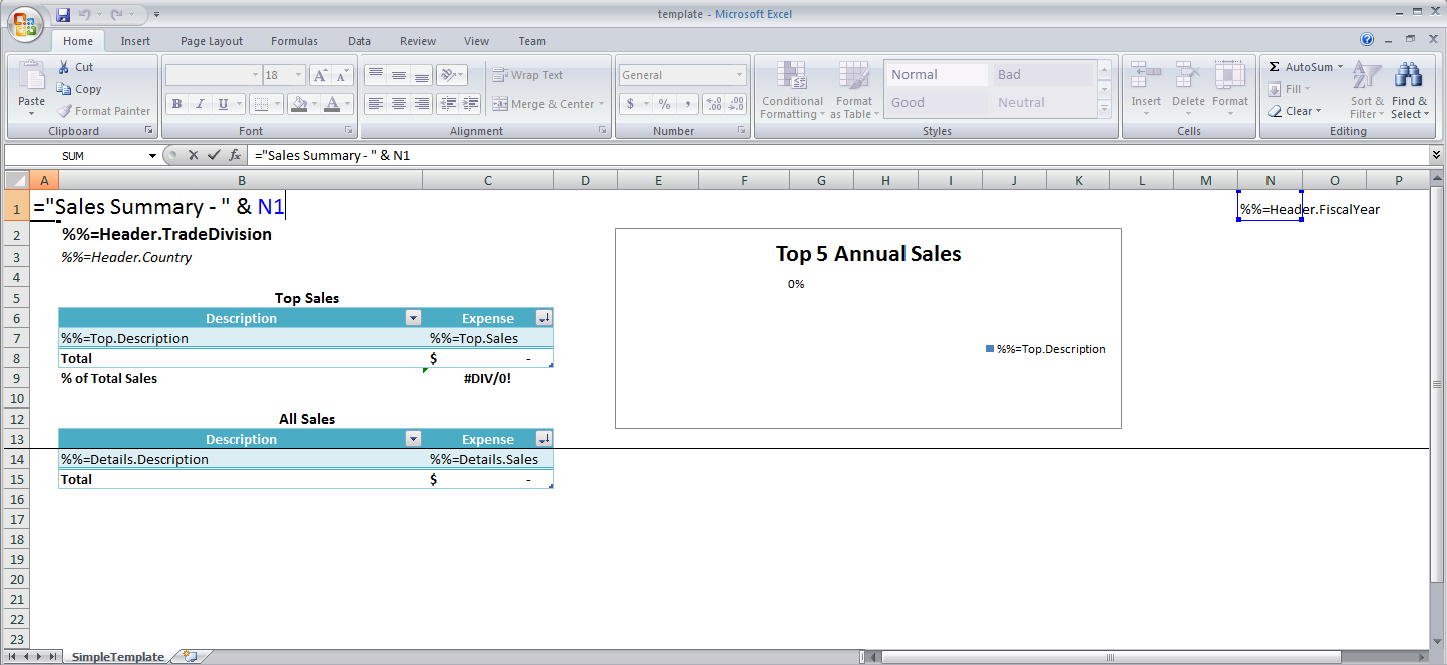
Cell N1 was hidden by using a custom format where the field was filled with ';;;'.
| Info |
|---|
In the sample code, the complete template file is located in ExtendedSalesSummary/templates/template.xlsx .The template is also available here. |
In the template, the %%=Header.FiscalYear data marker is concatenated with "Sales Summary -". Data markers cannot be used directly in formulas; the data marker needs to be in a separate cell, which can be referenced in an Excel formula.
In the header, there is a formula =CONCATENATE("Sales Summary - ", N1), where N1 is the cell that actually contains the %%=Header.FiscalYear data marker. This is shown in the image below.

Adding an ExcelWriter Reference in Visual Studio
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the sample code, the reference to |
Create To create a .NET project and add a reference to the ExcelWriter library.:
- Open Visual Studio and create a .NET project.
- The sample code uses a web application.
- Add a reference to SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter.dll
SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter.dllis located under under Program Files > SoftArtisans > OfficeWriter > dotnet > bin
Writing the Code
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The code behind for this |
...
Main function
part of the tutorial can be found under Extended Sales Summary/Part1.aspx.cs. |
There are two main sections of code that will be covered:
ExcelApplicationcode to customize the template based on a list of countries that a user has selected- In the sample, this code is contained in the
GenerateTemplate()method
- In the sample, this code is contained in the
ExcelTemplatecode to bind data to the customized template- In the sample, this code is contained in the
PopulateTemplate()method
- In the sample, this code is contained in the
Getting Started
1. Include the SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter namespace in the code behind:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
using SoftArtisans.Office.ExcelWriter; |
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
If you are following along and intend to use AdventureWorks2008R2, you will also want to make a reference to
|
2. In the method that will run the report2. At the top of the class definition, define global variations for the ExcelApplication, ExcelTemplate, and Workbook objects:
| Code Block |
|---|
private ExcelApplication xla;
private ExcelTemplate xlt;
private Workbook wb;
|
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the sample code, you will also see |
Customizing the template
1. Define a method to contain the ExcelApplication code for customizing the sheet. In the sample, this method is called GenerateTemplate()
| Code Block |
|---|
//Use ExcelApplication to make a copy of a regional worksheet for each
//country that is selected by the user.
protected void GenerateTemplate()
{
}
|
2. In the helper method, instantiate the ExcelApplication object.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
ExcelApplication xla = new ExcelApplication(); |
3. Open the ExcelApplication object Workbook template file with the ExcelApplication.Open() method and instantiate it as a Workbook object.
| Code Block |
|---|
Workbook wb = xla.Open(Page.MapPath(@"templates\template.xlsx")); |
4. Assuming that you taking the selections from a ASP.NET ListBox, use the following utility method to create a string list of all the countries that were selected.
| Code Block |
|---|
protected List<string> GetListBoxSelections(){
//Get the ListBox selections and make the appropriate number of copies
List<string> countryNames = new List<string>();
foreach (int i in ListBox1.GetSelectedIndices())
{
countryNames.Add(ListBox1.Items[i].Text);
}
return countryNames;
} |
| Info |
|---|
A utility method refers to a piece of code/function that is not affected by the ExcelWriter API framework. For the purpose of this tutorial, utility methods will be included as a separate function outside of the Main function. |
5. ExcelApplication can make copies of a specified worksheet using the Worksheets.CopySheet() method. This method requires a Worksheet object representing the sheet to be copied; an integer representing the new worksheet's position and, the string representing the name of the new worksheet.
Insert the following code that iterates through the selected countries in the string list to make copies of the "SimpleTemplate" in the original template.xlsx file. Each new worksheet is placed after the "SimpleTemplate" sheet and is named based on the selected country from the string list. The <i>for<i> loop uses the <i>List<i>.Count method to determine how many copies must be made.
...
In the sample, the user selects anywhere from 1-4 countries to include in the report. The selected countries are stored in the List<string> object, selectedCountries. For each country, make a copy of the basic template sheet with Worksheets.CopySheet(), place the copied worksheet at the end of the workbook, and give the new sheet a name.
In this example, the sheet that needs to be copied is the first worksheet in the template file. It can be accessed through Workbook.Worksheets by index (0) or by name ("SimpleTemplate").
| Code Block |
|---|
for (int i = 0; i < selectedCountries.Count; i++)
{
wb.Worksheets.CopySheet(wb.Worksheets[0], wb.Worksheets.Count, selectedCountries[i]);
}
|
6. At this point , there is the workbook contains a worksheet named after each selected country and in addition to the original worksheet contained in the wb Workbook object. We need to hide the original worksheet using the . Hide the original template sheet by setting Worksheet.Visibility method. This method can also make a worksheet 'visible' or 'very hidden.'
| Code Block |
|---|
wb.Worksheets[0].Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden; |
7. Select the first visible worksheet after the now hidden one to be displayed when the file first is opened using the Worksheets.Select() method.
| Code Block |
|---|
wb.Worksheets[1].Select(); |
8. Instantiate a new ExcelTemplate object.The final code for the GenerateTemplate() method should look like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
ExcelTemplateprotected xlt void GenerateTemplate() { xla = new ExcelTemplateExcelApplication(); |
9. Open the ExcelApplication workbook using the ExcelTemplate.Open(ExcelApplication, Workbook) method.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.Open(xla, wb); |
10. The use of function in an ExcelWriter code file is sometimes the most efficient way to approach a situation. In this case, a separate function is created to bind the data. This function is called in a for loop that is contained with the other code. Let the function that deals with data binding be called BindCountryData() and takes a worksheets name's as a string parameter.
| Code Block |
|---|
for wb = xla.Open(Page.MapPath(@"templates\template.xlsx")); for (int i = 0; i < wbselectedCountries.Worksheets.Count; i++) { wb.Worksheets.CopySheet(wb.Worksheets[0], wb.Worksheets.Count, selectedCountries[i]); } BindCountryData( wb.Worksheets[i].Name"SimpleTemplate"].Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden; wb.Worksheets[1].Select(); } |
| Info |
|---|
We will return to this function after completing the main code. |
...
Binding Data Dynamically
1. Define a method to contain the ExcelTemplate code for binding the data to the template. In the sample, this method is called PopulateTemplate()
| Code Block |
|---|
//Use ExcelTemplate to bind data for each selected country
//to worksheets in the template, then populate the report
//with that data
protected void PopulateTemplate()
{
}
|
2. In the helper method, instantiate a new ExcelTemplate object.
| Code Block |
|---|
ExcelTemplate xlt = new ExcelTemplate(); |
3. Pass the existing ExcelApplication and Workbook to the ExcelTemplate object using ExcelTemplate.Open(ExcelApplication, Workbook).
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.ProcessOpen(xla, wb); |
12. Call 4. Although not necessary, it may be useful to set ExcelTemplate.Save to save the output file.ExcelTemplate has several output options: save to disk, save to a stream, stream the output file in a page's Response inline or as an attachmentRemoveExtraDataMarkers to true. This will tell ExcelWriter to ignore any data markers that are not bound to data sets. This is helpful if you are adding the data binding calls to the code one at a time.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false); |
BindCountryData function
...
RemoveExtraDataMarkers = true; |
5. For each selected country, data needs to be bound to the corresponding worksheet. Define a DataBindingProperties object for future use and set up a for loop to go through all the selected countries.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataBindingProperties protecteddataBindProps; void protectedfor void BindCountryData(string selection){} |
2. Create a DataBindingProperty based on the Worksheet name. DataBindingProperties is like a tag used to specify how data is bound to a worksheet.
Other DataBindingProperties include MaxRows and Transpose.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataBindingProperties dbp int i = 0; i < selectedCountries.Count; i++) { } |
The next few steps relate to code contained in the for loop.
For each selected country:
6. Retrieve the name of the country.
| Code Block |
|---|
string country = selectedCountries[i]; |
7. Instantiate a new DataBindingProperties object.
| Code Block |
|---|
dataBindProps = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties(); dbp.WorksheetName = selection; |
...
8. When a data set is bound to an Excel template, any data markers with matching syntax will be populated with the data from that data set. This can be problematic if your template contains copied sheets, where all the data markers are identical.
To get around this, set the DataBindingProperties.WorksheetName to bind a data set only to a particular worksheet.
| Code Block |
|---|
dataBindProps.WorksheetName = country; |
9. Create an string array for the header values and a string array for the column names.
...
Some of the aforementioned structures have built in column names, such as the DataTable. When working with arrays, which don't have built in column names, you have to define the column names in a separate string array.
| Code Block |
|---|
string[] specificInfoheaderValues = { "FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", selectioncountry }; string[] headerTitlesheaderNames = { "FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" }; |
410. Use the ExcelTemplate.BindRowData method to bind the header data to the data markers in the template file (%%=Header.FiscalYear, %%=Header.TradeDivision, i.e. %%=Header.CountryFiscalYear).
BindRowData() binds a single row of data to the template, but the data markers in the template do not need to be in a single row.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.BindRowData(specificInfo, headerTitles, "Header", dbpdataBindProps); |
511. Get the data for the Top 5 Expenses and All Expenses Details Sales data sets.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataTable dts = Sales(selection, "TOP 5");
DataTable dts2 = Sales(selection, "");
|
In this tutorial, it is assumed that your machine is equipped with AdventureWorks2008R2, and therefore that a SQL query is a valid operation. As a utility method, the following function will be included as a function outside of the Main and BindCountryData functions.
| Code Block |
|---|
public static DataTable Sales(string selection, string topORall)
{
//Create the query
string queryString = "USE AdventureWorks2008R2; " +
"DECLARE @find nvarchar(100); " +
"SET @find ='" + selection + "'; " +
"SELECT " + topORall + " Sales.Store.Name AS Description, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TotalDue AS Sales FROM Sales.Store " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.Customer ON Sales.Store.BusinessEntityID = Sales.Customer.StoreID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.Customer.CustomerID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.CustomerID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID = Sales.Customer.TerritoryID " +
"WHERE DATEPART(yyyy, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate) = 2008 " +
"AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OnlineOrderFlag = 0 " +
"AND Sales.SalesTerritory.Name = @find " +
"ORDER BY Sales DESC;";
//Get connection
SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(@"Data Source=TS-IH03\SQL2008R2;Initial Catalog=ExcelApp2;Integrated Security=True");
//Assign command and associated connection
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(queryString, connection);
//Select data adapter
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
//Make a new table, fill it and return it
DataTable dtGet = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(dtGet);
return dtGet;
}
|
| Info |
|---|
If you do not have AdventureWorks2008R2, you may download the sample file here. The sample code uses a utility method called GetCSVData to obtain data from the supplied CSV files. |
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
In the sample project, we are parsing CSV files with query results, rather than querying a live database. The CSV files are available under the data directory. There is a copy of the CSV parser, |
These calls are to a helper method GetCSVData that parses the CSV files and returns a DataTable with the values.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataTable dts = GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "5.csv"));
DataTable dts2 = GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "All.csv"));
|
If you are following in your own project and would like to parse the CSV files as well, you will need to:
- Add a reference to
GenericParsing.dll - Include
GeneringParsingat the top of your code. - Add the
GetCSVDatamethod that can be found in the sample code.
12. Use ExcelTemplate.BindData to bind the data for the Top and Details Sales data sets.
Recall that the data source names (Top, Details) need to match the data marker names exactly.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dbp);
xlt.BindData(dts2, "Details", dbp);
|
7. Now you may run your code.
Here is an example of what the sample will look like:
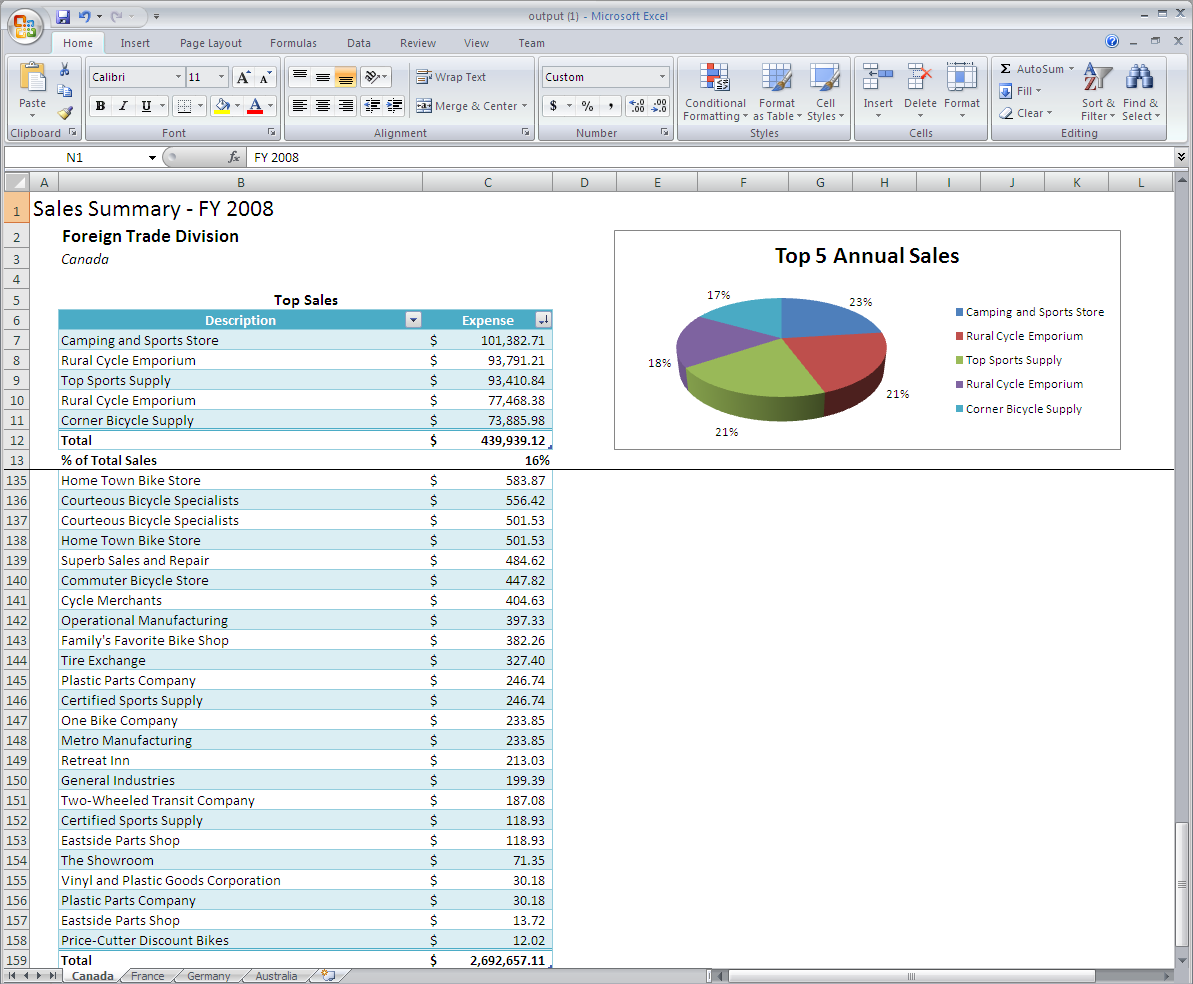
Note that there are multiple worksheets, each named for each country and containing it's specified data.
Final Code
...
13. The final for loop should look like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
for (int i = 0; i < selectedCountries.Count; i++) { string country wb.Worksheets.CopySheet(wb.Worksheets[0], wb.Worksheets.Count, = selectedCountries[i]); } wb.Worksheets[0].Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden; wb.Worksheets[1].Select(); xlt = new ExcelTemplate(); xlt.Open(xla, wb); for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++) { BindCountryData(wb.Worksheets[i].Name); } xlt.Process(); xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false); } protected void BindCountryData(string selection) { DataBindingProperties dbp = xlt.dataBindProps = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties(); dbpdataBindProps.WorksheetName = selectioncountry; string[] specificInfoheaderValues = { "FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", selectioncountry }; string[] headerTitlesheaderNames = { "FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" }; xlt.BindRowData(specificInfoheaderValues, headerTitlesheaderNames, "Header", dbpdataBindProps); DataTable dts = Sales(selection, "TOP 5")GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "5.csv")); DataTable dts2 = Sales(selection, ""); GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "All.csv")); xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dbpdataBindProps); xlt.BindData(dts2, "Details", dbpdataBindProps); } public static DataTable Sales(string selection, string topORall) } |
14. Call ExcelTemplate.Process() to import all data into the file.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.Process(); |
15. Call ExcelTemplate.Save to save the output file.
ExcelTemplate has several output options: save to disk, save to a stream, stream the output file in a page's Response inline or as an attachment.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false); |
16. The final code for PopulateTemplate() should look like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
protected void PopulateTemplate() { { xlt = new ExcelTemplate(); //Create thea querynew ExcelTemplate object string queryString = "USE AdventureWorks2008R2; " + "DECLARE @find nvarchar(100 xlt.Open(xla, wb); " + "SET @find ='" + selection + "'; " +xlt.RemoveExtraDataMarkers = true; DataBindingProperties dataBindProps; "SELECT " + topORall + " Sales.Store.Name AS Description, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TotalDue ASfor Sales(int i = 0; i FROM Sales.Store " +< selectedCountries.Count; i++) { "INNER JOIN Sales.Customer ON Sales.Store.BusinessEntityID = Sales.Customer.StoreID " + string "INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.Customer.CustomerID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.CustomerID " +country = selectedCountries[i]; "INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID = Sales.Customer.TerritoryID " +dataBindProps = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties(); "WHERE DATEPART(yyyy, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate)dataBindProps.WorksheetName = 2008country; " + string[] "AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OnlineOrderFlag headerValues = 0{ " + "AND Sales.SalesTerritory.Name = @find " + "ORDER BY Sales DESC;";FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", country }; //Get connection string[] SqlConnection connection headerNames = new{ SqlConnection(@"Data Source=TS-IH03\SQL2008R2;Initial Catalog=ExcelApp2;Integrated Security=True")"FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" }; //Assign command and associated connection SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(queryString, connection xlt.BindRowData(headerValues, headerNames, "Header", dataBindProps); //Select data adapter DataTable SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter(); adapter.SelectCommand = cmd; //Make a new table, fill it and return itdts = GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "5.csv")); DataTable dtGetdts2 = new DataTable(); adapter.Fill(dtGet)GetCSVData(Page.MapPath("//data//" + country + "All.csv")); return dtGet; } protected List<string> GetListBoxSelections(){ //Get the ListBox selections and make the appropriate number of copies List<string> countryNames = new List<string>(xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dataBindProps); foreach (int i in ListBox1xlt.GetSelectedIndicesBindData()) dts2, "Details", dataBindProps); { } countryNamesxlt.Add(ListBox1.Items[i].TextProcess(); } return countryNames; } xlt.Save(Page.Response, "Output.xlsx", false); } |
17. Now you may run your code. Just call GenerateTemplate() and PopulateTemplate() to customize and populate your template.
Here is an example of what the sample will look like:

Note that there are multiple worksheets, each with the tab name and data for that region.
Downloads
You can download the code for the Extended Sales Summary here.