...
The code for this report uses two functions- the Main function and the BindCountryData functions. The Main function calls the BindCountryData function taking each country's worksheet as a parameter. See below for further explanation.
Main function
1. Include the SoftArtisans.OfficeWriter.ExcelWriter namespace in the code behind
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
If you are following along and intend to use AdventureWorks2008R2, you will also want to make a reference to
|
2. In the method that will run the report, instantiate the ExcelApplication object.
...
| Code Block |
|---|
Workbook wb = xla.Open(Page.MapPath(@"templates\template.xlsx")); |
4. Assuming that you taking the selections from a ASP.NET ListBox, use the following utility method to create a string list of all the countries that were selected.
...
| Info |
|---|
A utility method refers to a piece of code/function that is not affected by the ExcelWriter API framework. For the purpose of this tutorial, utility methods will be included as a separate function outside of the Main function. |
5. ExcelApplication can make copies of a specified worksheet using the Worksheets.CopySheet() method. This method requires a Worksheet object representing the sheet to be copied; an integer representing the new worksheet's position and, the string representing the name of the new worksheet.
...
10. The use of function in an ExcelWriter code file is sometimes the most efficient way to approach a situation. In this case, a separate function is created to bind the data. This function is called in a for loop that is contained with the other code. Let the function that deals with data binding be called BindCountryData() and takes a worksheets name's as a string parameter.
| Code Block |
|---|
for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
BindCountryData(wb.Worksheets[i].Name);
}
|
...
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false); |
BindCountryData function
1. Create a function called BindCountryData that takes a string parameter called selection.
| Code Block |
|---|
protected void protected void BindCountryData(string selection){}
|
2. Create a DataBindingProperty based on the Worksheet name. DataBindingProperties is like a tag used to specify how data is bound to a worksheet.
Other DataBindingProperties include MaxRows and Transpose.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataBindingProperties dbp = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties();
dbp.WorksheetName = selection; |
3. Create an string array for the header values and a string array for the column names.
ExcelTemplate can be bound to numerous types of .NET data structures: single variables, arrays (1-D, jagged, multi-dimensional), DataSet, DataTable, IDataReader etc. The source of the data can come from anywhere.
Some of the aforementioned structures have built in column names, such as the DataTable. When working with arrays, which don't have built in column names, you have to define the column names in a separate string array.
| Code Block |
|---|
string[] specificInfo = { "FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", selection };
string[] headerTitles = { "FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" }; |
4. Use the ExcelTemplate.BindRowData method to bind the header data to the data markers in the template file (%%=Header.FiscalYear, %%=Header.TradeDivision, %%=Header.Country).
BindRowData() binds a single row of data to the template, but the data markers in the template do not need to be in a single row.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.BindRowData(specificInfo, headerTitles, "Header", dbp); |
5. Get the data for the Top 5 Expenses and All Expenses data sets.
| Code Block |
|---|
DataTable dts = Sales(selection, "TOP 5");
DataTable dts2 = Sales(selection, "");
|
In this tutorial, it is assumed that your machine is equipped with AdventureWorks2008R2, and therefore that a SQL query is a valid operation. As a utility method, the following function will be included as a function outside of the Main and BindCountryData functions.
| Code Block |
|---|
public static DataTable Sales(string selection, string topORall)
{
//Create the query
string queryString = "USE AdventureWorks2008R2; " +
"DECLARE @find nvarchar(100); " +
"SET @find ='" + selection + "'; " +
"SELECT " + topORall + " Sales.Store.Name AS Description, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TotalDue AS Sales FROM Sales.Store " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.Customer ON Sales.Store.BusinessEntityID = Sales.Customer.StoreID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.Customer.CustomerID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.CustomerID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID = Sales.Customer.TerritoryID " +
"WHERE DATEPART(yyyy, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate) = 2008 " +
"AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OnlineOrderFlag = 0 " +
"AND Sales.SalesTerritory.Name = @find " +
"ORDER BY Sales DESC;";
//Get connection
SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(@"Data Source=TS-IH03\SQL2008R2;Initial Catalog=ExcelApp2;Integrated Security=True");
//Assign command and associated connection
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(queryString, connection);
//Select data adapter
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
//Make a new table, fill it and return it
DataTable dtGet = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(dtGet);
return dtGet;
}
|
| Info |
|---|
If you do not have AdventureWorks2008R2, you may download the sample file here. The sample code uses a utility method called GetCSVData to obtain data from the supplied CSV files. |
6. Use ExcelTemplate.BindData to bind the data for the Top and Details Sales data sets.
Recall that the data source names (Top, Details) need to match the data marker names exactly.
| Code Block |
|---|
xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dbp);
xlt.BindData(dts2, "Details", dbp);
|
7. Now you may run your code.
Here is an example of what the sample will look like:
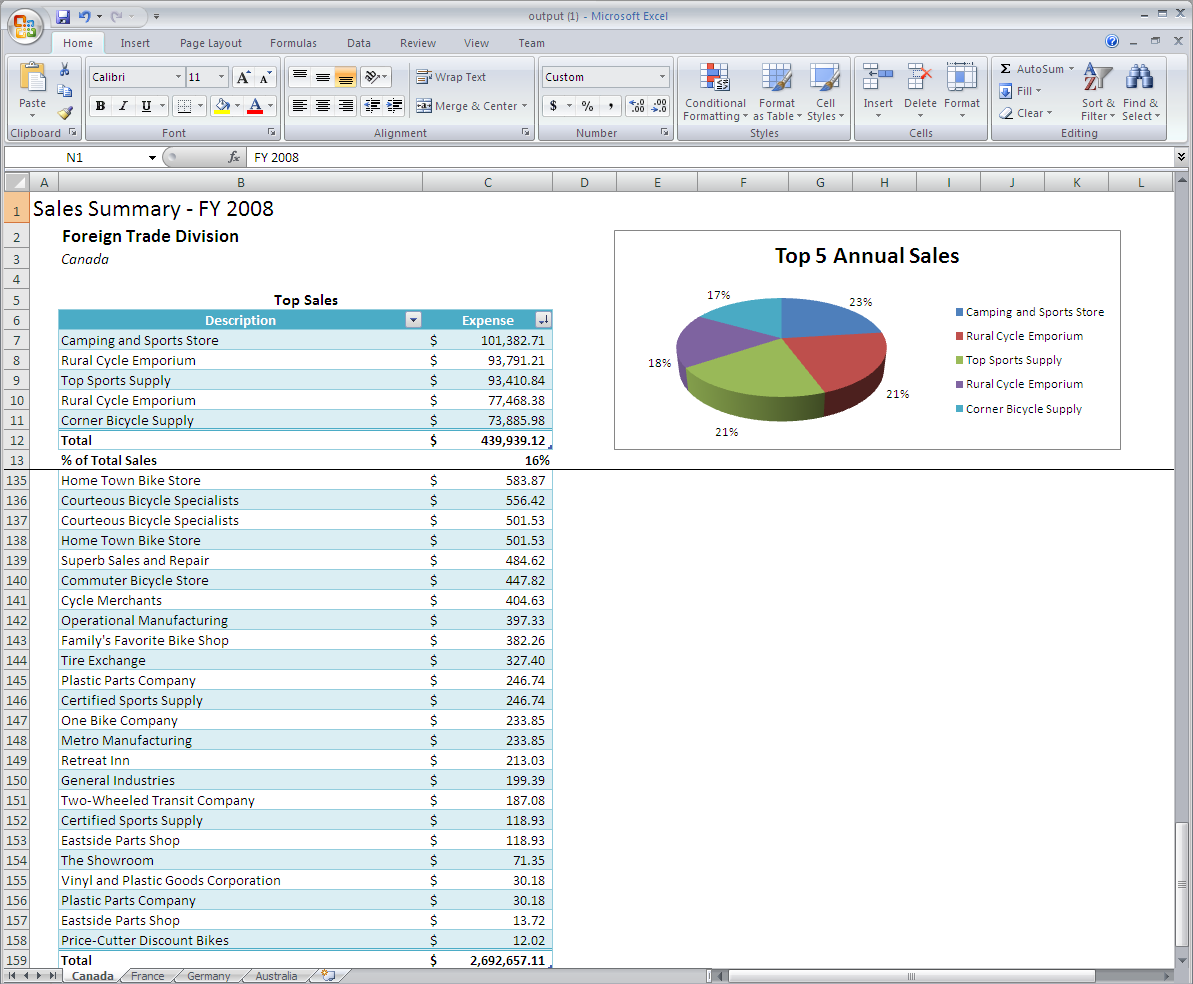
Note that there are multiple worksheets, each named for each country and containing it's specified data.
Final Code
| Code Block |
|---|
using SoftArtisans.Office.ExcelWriter;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Collections.Generic;
...
protected void Main(object sender, EventArgs e){
ExcelApplication xla = new ExcelApplication();
Workbook wb = xla.Open(Page.MapPath(@"templates\template.xlsx"));
for (int i = 0; i < selectedCountries.Count; i++)
{
wb.Worksheets.CopySheet(wb.Worksheets[0], wb.Worksheets.Count, selectedCountries[i]);
}
wb.Worksheets[0].Visibility = Worksheet.SheetVisibility.Hidden;
wb.Worksheets[1].Select();
xlt = new ExcelTemplate();
xlt.Open(xla, wb);
for (int i = 0; i < wb.Worksheets.Count; i++)
{
BindCountryData(wb.Worksheets[i].Name);
}
xlt.Process();
xlt.Save(Page.Response, "output.xlsx", false);
}
protected void BindCountryData(string selection)
{
DataBindingProperties dbp = xlt.CreateDataBindingProperties();
dbp.WorksheetName = selection;
string[] specificInfo = { "FY 2008", "Foreign Trade Division", selection };
string[] headerTitles = { "FiscalYear", "TradeDivision", "Country" };
xlt.BindRowData(specificInfo, headerTitles, "Header", dbp);
DataTable dts = Sales(selection, "TOP 5");
DataTable dts2 = Sales(selection, "");
xlt.BindData(dts, "Top", dbp);
xlt.BindData(dts2, "Details", dbp);
}
public static DataTable Sales(string selection, string topORall)
{
//Create the query
string queryString = "USE AdventureWorks2008R2; " +
"DECLARE @find nvarchar(100); " +
"SET @find ='" + selection + "'; " +
"SELECT " + topORall + " Sales.Store.Name AS Description, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TotalDue AS Sales FROM Sales.Store " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.Customer ON Sales.Store.BusinessEntityID = Sales.Customer.StoreID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.Customer.CustomerID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.CustomerID " +
"INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID = Sales.Customer.TerritoryID " +
"WHERE DATEPART(yyyy, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate) = 2008 " +
"AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OnlineOrderFlag = 0 " +
"AND Sales.SalesTerritory.Name = @find " +
"ORDER BY Sales DESC;";
//Get connection
SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(@"Data Source=TS-IH03\SQL2008R2;Initial Catalog=ExcelApp2;Integrated Security=True");
//Assign command and associated connection
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(queryString, connection);
//Select data adapter
SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
//Make a new table, fill it and return it
DataTable dtGet = new DataTable();
adapter.Fill(dtGet);
return dtGet;
}
protected List<string> GetListBoxSelections(){
//Get the ListBox selections and make the appropriate number of copies
List<string> countryNames = new List<string>();
foreach (int i in ListBox1.GetSelectedIndices())
{
countryNames.Add(ListBox1.Items[i].Text);
}
return countryNames;
}
|
Downloads
You can download the code for the Extended Sales Summary here.
- boom